
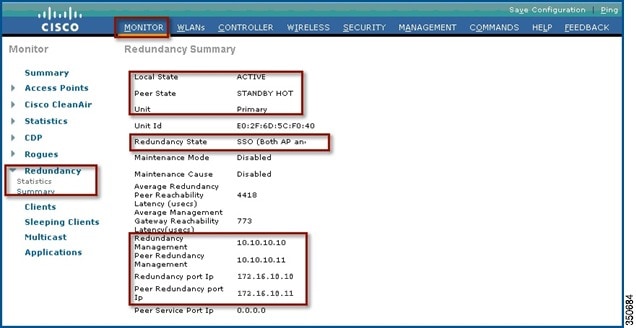
Section in the High Availability (SSO) Deployment Guide at: For additional client SSO behaviors and limitations, see the "Client SSO" To the controller following an HA SSO switchover. Switched over to the standby controller without interruption, except PMIPv6 clients, which will need to reconnect and authenticate The reason or cause for most switchoverĮvents is due to a manual trigger, a controller and/or a network failure.ĭuring an HA SSO failover event, all of the AP CAPWAP sessions and client sessions in RUN state on the controller are statefully The primary and the secondary controllers. After subsequent switchovers, the roles are interchanged between After a switchover, the secondaryĬontroller becomes the active controller and the primary controller becomes the Role of the secondary controller as standby-hot. The boot process, the role of the primary controller is negotiated as active and the In a High Availability architecture, one controller is configured as the primaryĬontroller and another controller as the secondary controller.Īfter you enable High Availability, the primary and secondary controllers are rebooted. High Availability in controllers allows you to reduce the downtime of the wireless networks thatĬould occur due to failover of controllers.Ī 1:1 (Active:Standby-Hot) stateful switchover of access points and clients is supported (HA Replacing the Primary Controller in an HA Setup.Monitoring High Availability Standby WLC.Adding a Hash Key to a Cisco vWLC (GUI).

Client Traffic Forwarding Configurations.Connecting Mesh Access Points to the Network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
